Step 1
The marginal benefit (MB) is the additional benefit received from purchasing one more unit of the good.
The marginal cost (MC) is the additional cost incurred on producing one more unit of the good.
The profit is maximized for the firm when it produces at the level at which the marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost as if firm produces at a output level at which MB is less than MC then firm can attain higher decreasing production and if firm produces at a level at which MB is more than MC then firm by increasing producing can increase the marginal net benefit.
Marginal benefit (MB) is the first derivative of Total benefit (TB) and is calculated as follows:
Marginal cost (MC) is the first derivative of total cost (C) and is calculated as follows:
A profit maximizing firm produces at the level at which marginal benefit (MB) equals marginal cost (MC).
Marginal Net Benefit (MNB) is the difference between marginal benefit and marginal cost.
The price is equal to the marginal benefit.
The difference between revenue and cost is profit and calculated as follows:
The table below shows the value of MB, MC, MNB and the profit is shown as follows:
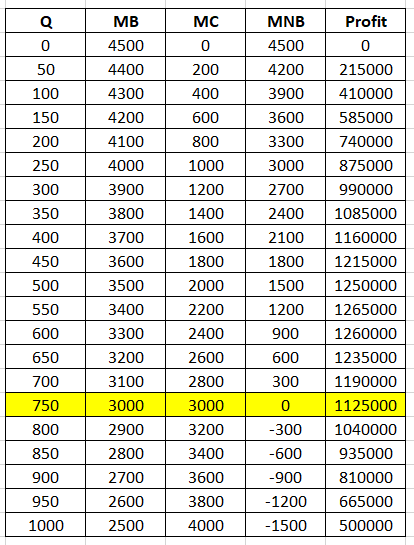
The marginal benefit (MB) equals to the marginal cost (MC) at 750 output level.
Thus, profit maximizing quantity is 750.