Link will be apear in 30 seconds.
Well done! you have successfully gained access to Decrypted Link.
Step 1
Assumption
- Horizontal shear acting on the inner column is equal to the double of horizontal shear on outer columns.
- Shear is acting at midpoint of each member.
Shear forces assumed on each member
IJ=R
JK=S
KL=T
IE=P
JF=2P
KG=2P
LH=P
EF=U
FG=V
GH=W
EA=Q
BF=2Q
CG=2Q
DH=Q
Step 2
Horizontal shear
For storey first
For bottom storey
Taking joint I
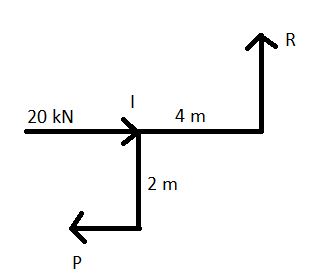
Taking joint J
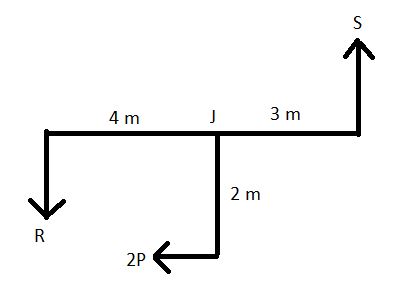
Taking joint K
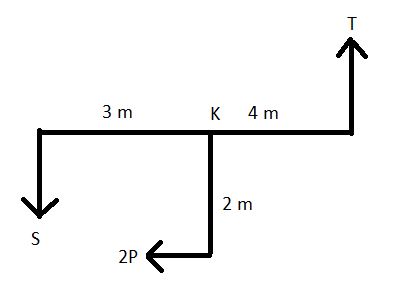
For bottom storey
Taking joint E
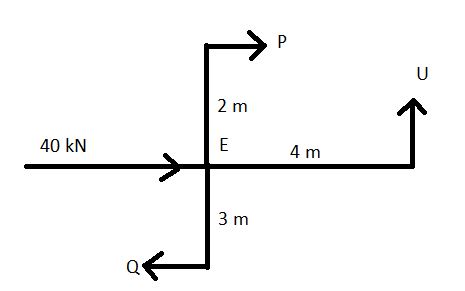
Taking joint F
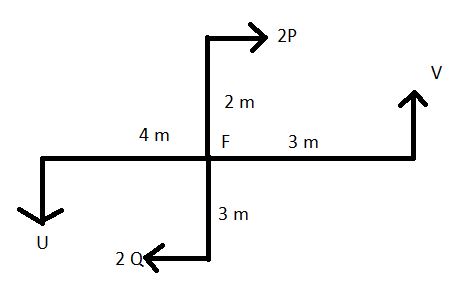
Taking joint G
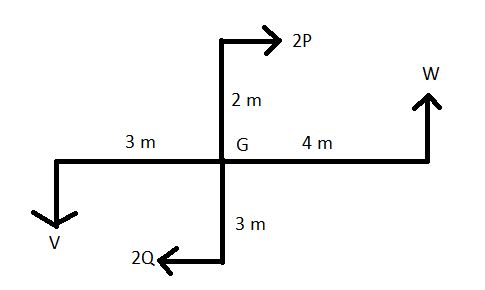
Shear forces
P= 3.33 kN
Q= 10 kN
R= 1.665 kN
S= 2.22 kN
T= 1.665 kN
U= 9.165 kN
V= 12.22 kN
W= 9.165 kN
Step 3
Axial force calculations
In column AEI
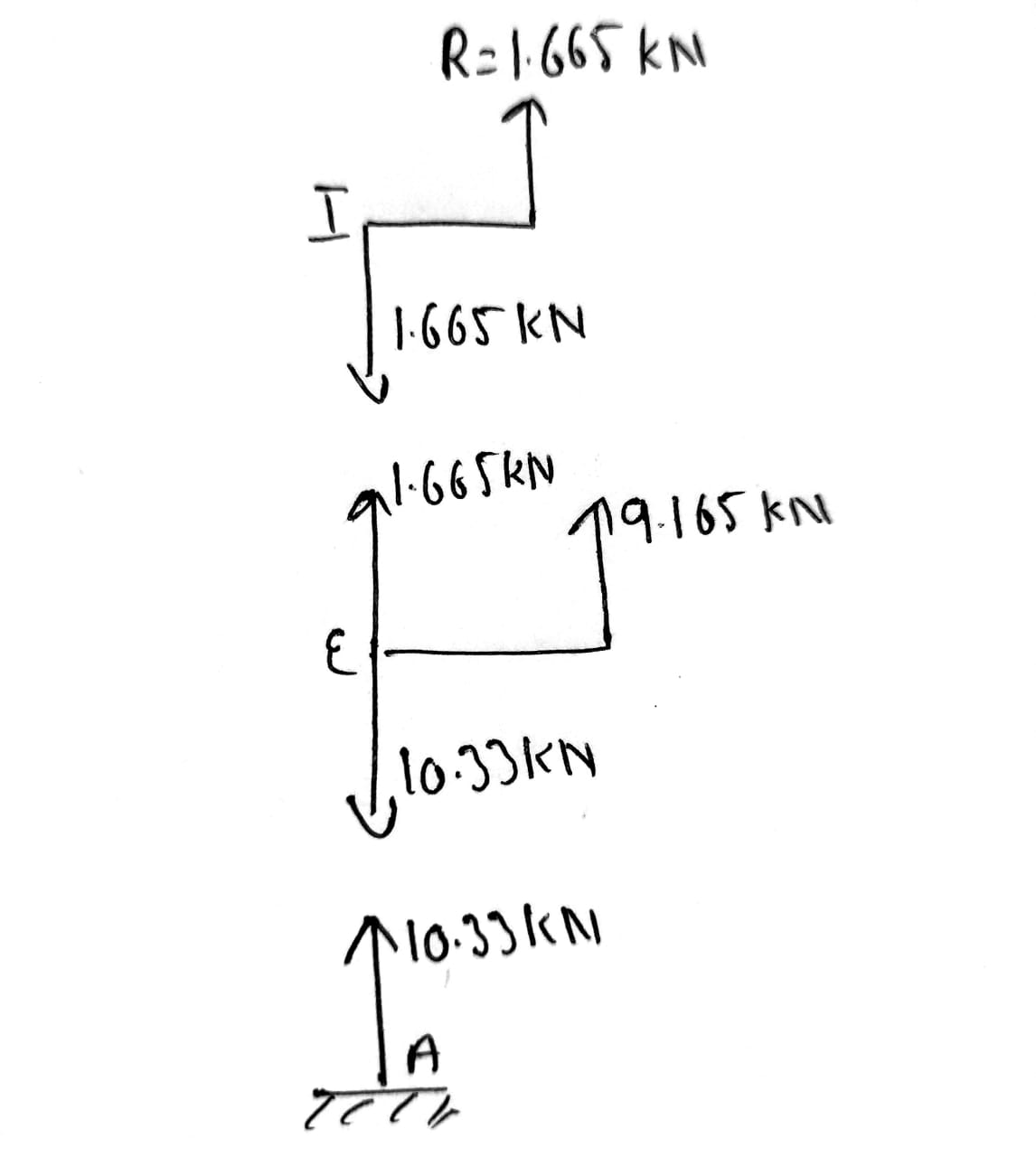
Axial force at AEI=10.33 kN
In column BFJ
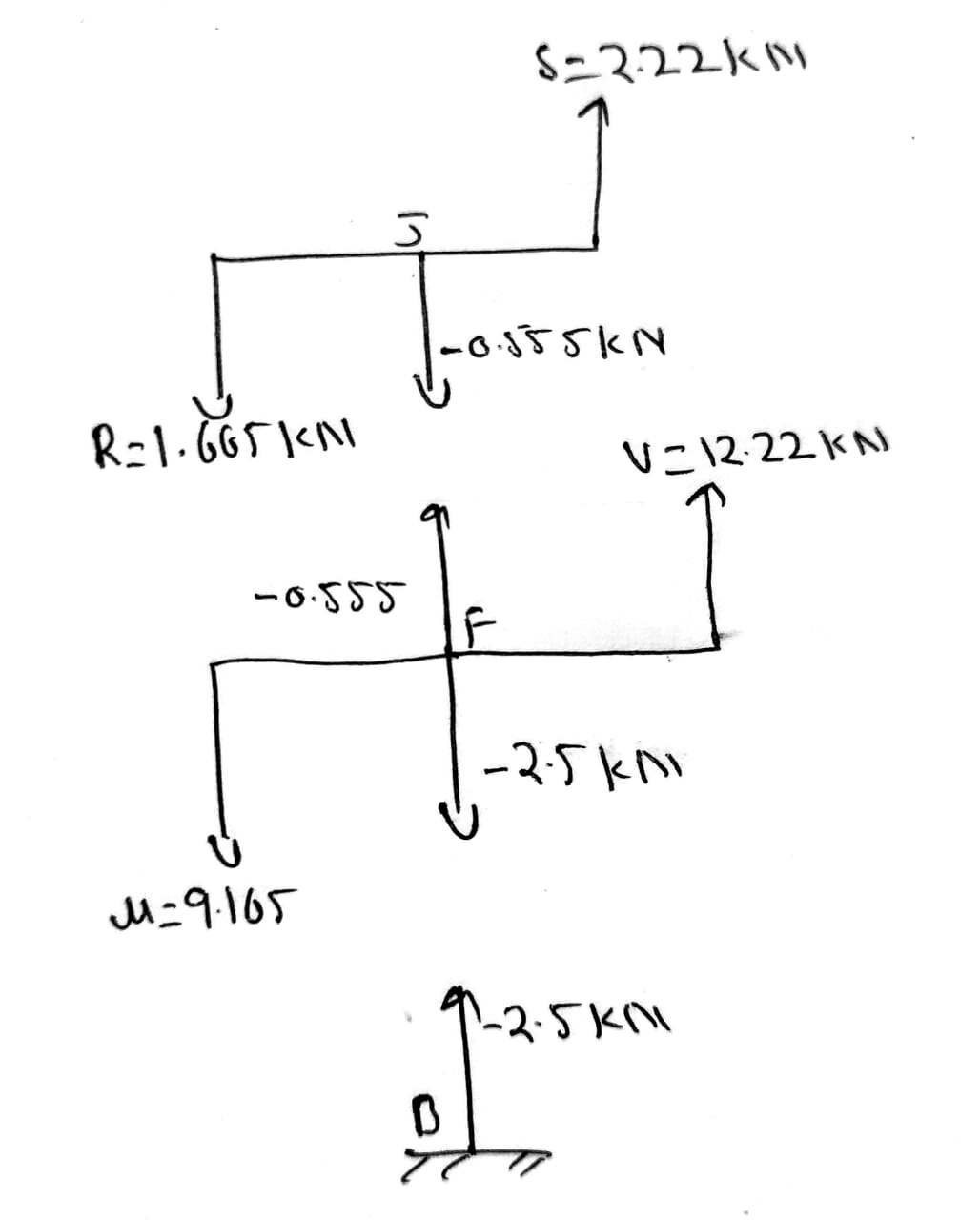
Axial force at BFJ=-2.5 kN (Upward direction)
In column CGK
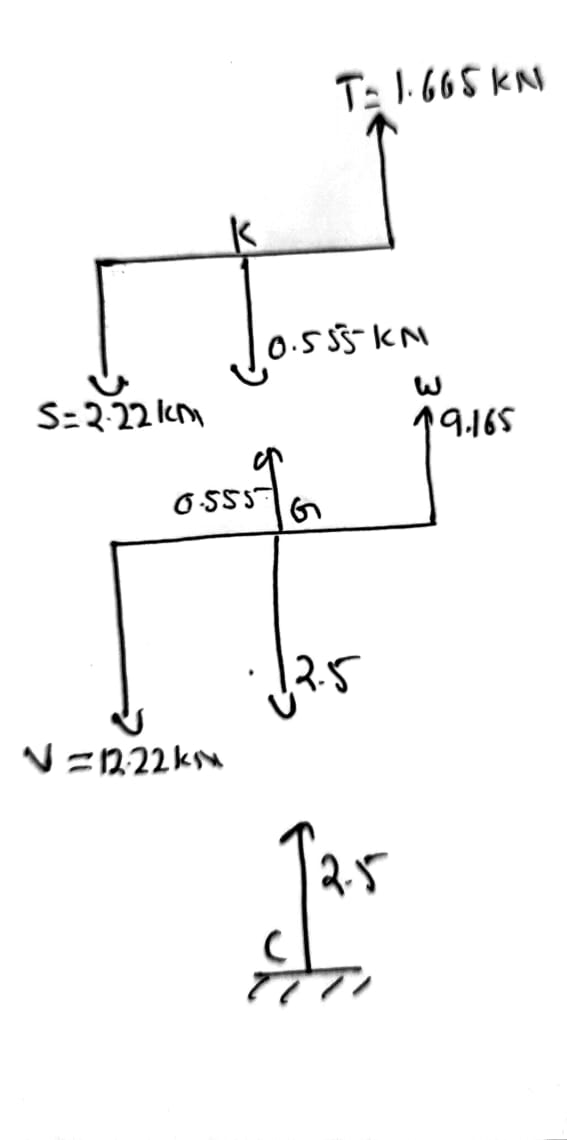
Axial force at CGK= 2.5 kN
In column DHL
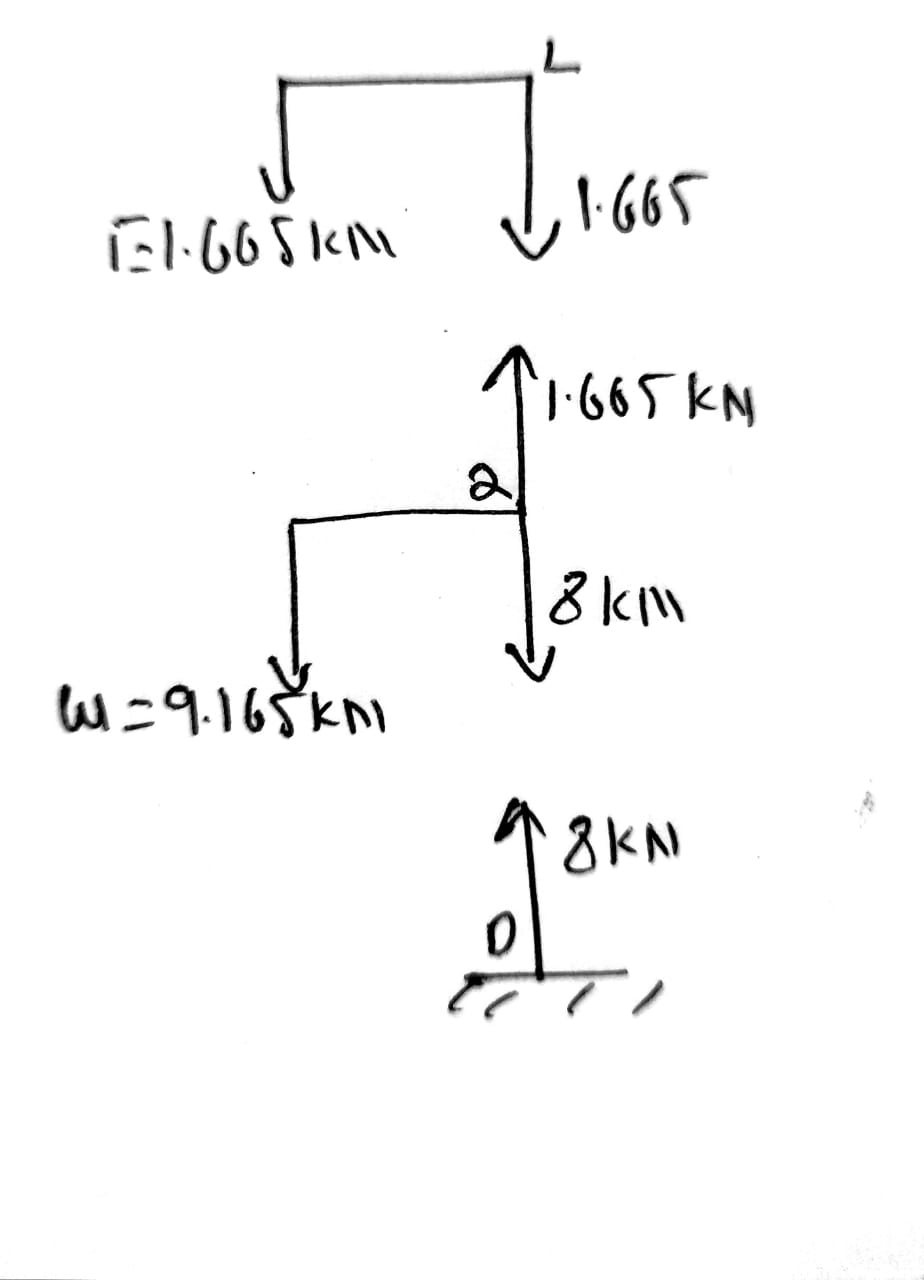
Axial force at DHL=8 kN