Rod AB is fixed to a smooth collar D, which slides freely along the vertical guide. Determine the internal normal force, shear force, and moment at point C, which is located just to the left of the 60-lb concentrated load.
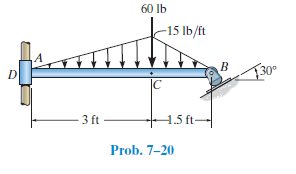
Image Transcriptionclose
60 lb -15 lb/ft F30° |C 3 ft 1.5 ft- Prob. 7-20
Consider the free body diagram of the member AB as shown below.
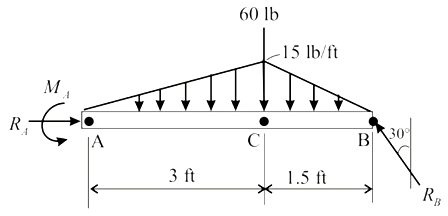
Consider the moment equilibrium about point B.
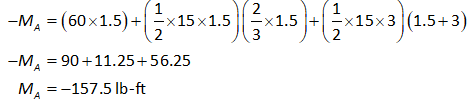
Consider the moment equilibrium at point A.
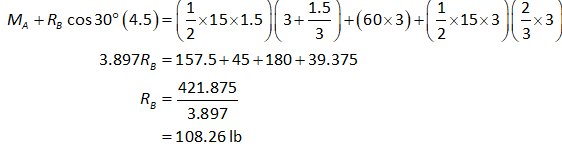
Consider the portion BC as shown below.
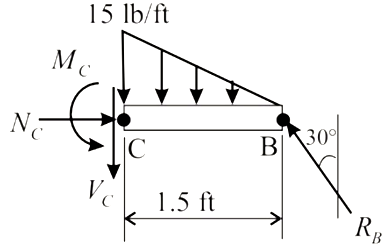
Here, NC is the normal force at point C, VC is the shear force at point C and MC is the moment at point C.
Consider the summation of forces in the horizontal direction.
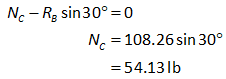
Consider the summation of forces in the vertical direction.
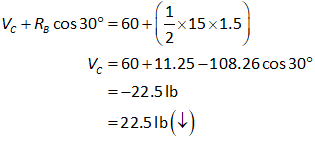
Consider the equilibrium moment about point C.
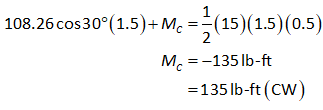
Therefore, at point C the normal force is 54.13 lb towards right, the shear force is 22.5 lb in the downward direction and the moment is 135 lb-ft in the clockwise direction.