Link will be apear in 30 seconds.
Well done! you have successfully gained access to Decrypted Link.
Question:
A hydraulic lift is to be used to lift a 550 kg weight, the piston–cylinder of the hydraulic lift contains oil at a pressure of 580 kPa. The piston has a mass of 6 kg and a diameter of 12 cm. In this case the local atmospheric pressure is a. 100 kPa b. 95.7 kPa c. 98 kPa d. None of these e. 96.3 kPa f. 97.3 kPa
Answer:
Step 1
Given:
- Mass of the body to lifted (M)=550kg
- Mass of the piston (m)=6kg
- Diameter of the piston (D)=12cm
- Pressure inside the piston cylinder (P)=580kPa
Step 2
Solution:
The pressure inside the piston cylinder will be equal to the sum of atmospheric pressure and pressure due to the weight of the object and piston,
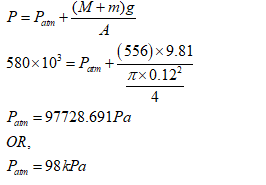
Therefore, local atmospheric pressure is 98kPa-option C is the answer.