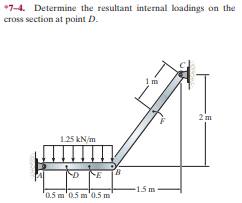
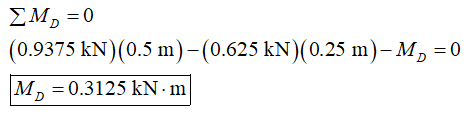Question:
Answer:
Step 1
The free body diagram of the section ADEB is,
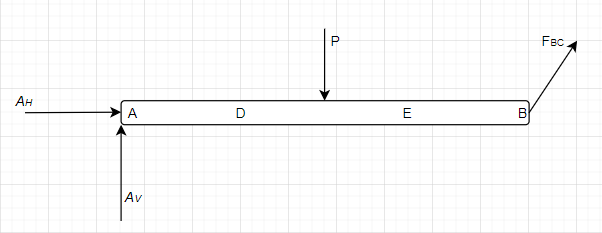
Here, P is the effective loading due to the UDL. H and V are the subscript for the horizontal and vertical reaction at A respectively.
Step 2
Calculate the value of effective loading due to the UDL, P,

Consider the angle B as θ and apply the condition for the equilibrium of moment about support A.
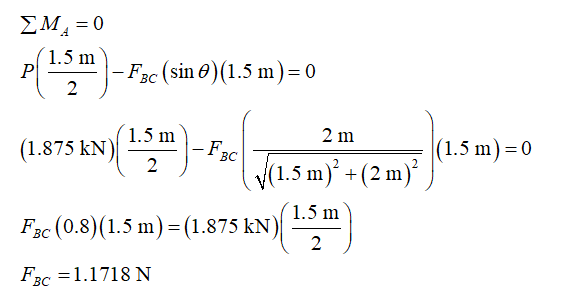
Step 3
Apply the condition for the equilibrium of forces along the vertical direction.
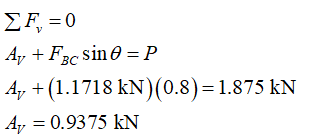
Step 4
Similarly, apply the condition for the equilibrium of forces along the horizontal direction.
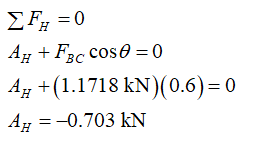
Step 5
Consider the FBD of the section AD of the beam,
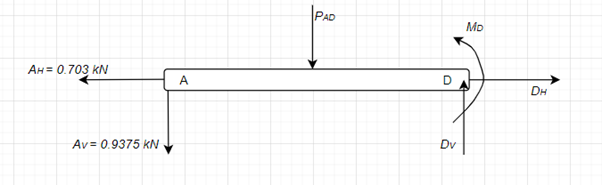
Calculate the effective load due to UDL, PAD acting on AD,

Step 6
Apply the condition for the equilibrium of forces along the vertical direction for the section AD.
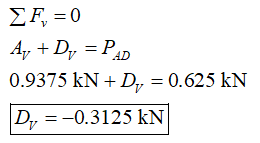
This the vertical reaction at point D.
Step 7
Apply the condition for the equilibrium of forces along the horizontal direction for the section AD.
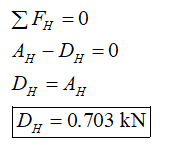
This the horizontal reaction at point D.
Step 8
Now, apply the condition for the equilibrium of moment about point D.